Índice de Contenidos
- Introduction
- Option –json
- Introduction to
gh api - Introduction to
gh alias - GraphQL Examples
- Extensions
- Running Manually GitHub Workflows with gh
- Cambiando los permisos de GITHUB_TOKEN
- References
Introduction
What is
gh pretends to facilitate the access to GitHub from the command line. It brings pull requests, issues, and other GitHub concepts to the terminal next to where you are already working with git and your code. For GitLab there is a similar tool called glab
Version
➜ markdown git:(master) ✗ gh --version
gh version 2.14.3 (2022-07-26)
https://github.com/cli/cli/releases/tag/v2.14.3
Help
➜ markdown git:(master) ✗ gh help
Work seamlessly with GitHub from the command line.
USAGE
gh <command> <subcommand> [flags]
CORE COMMANDS
auth: Authenticate gh and git with GitHub
browse: Open the repository in the browser
codespace: Connect to and manage codespaces
gist: Manage gists
issue: Manage issues
pr: Manage pull requests
release: Manage releases
repo: Manage repositories
ACTIONS COMMANDS
run: View details about workflow runs
workflow: View details about GitHub Actions workflows
ADDITIONAL COMMANDS
alias: Create command shortcuts
api: Make an authenticated GitHub API request
completion: Generate shell completion scripts
config: Manage configuration for gh
extension: Manage gh extensions
gpg-key: Manage GPG keys
help: Help about any command
label: Manage labels
search: Search for repositories, issues, and pull requests
secret: Manage GitHub secrets
ssh-key: Manage SSH keys
status: Print information about relevant issues, pull requests, and notifications across repositories
HELP TOPICS
actions: Learn about working with GitHub Actions
environment: Environment variables that can be used with gh
formatting: Formatting options for JSON data exported from gh
mintty: Information about using gh with MinTTY
reference: A comprehensive reference of all gh commands
EXTENSION COMMANDS
FLAGS
--help Show help for command
--version Show gh version
EXAMPLES
$ gh issue create
$ gh repo clone cli/cli
$ gh pr checkout 321
LEARN MORE
Use 'gh <command> <subcommand> --help' for more information about a command.
Read the manual at https://cli.github.com/manual
FEEDBACK
Open an issue using 'gh issue create -R github.com/cli/cli'
Installation
To install it, see the installation instructions.
Check the GitHub CLI Manual for more details.
There are several ways you can extend/customize gh:
- Create shorthands using
gh alias set - Make custom API queries using
gh api - Use environment variables
Option –json
Some gh commands support exporting the data as JSON as an alternative to their usual line-based plain text output.
This is suitable for passing structured data to scripts. The JSON output is enabled with the --json option, followed by the list of fields to fetch.
Use the flag without a value to get the list of available fields.
$ gh issue list
Showing 2 of 2 open issues in crguezl/learning-graphql-with-gh
#2 second issue about 6 days ago
#1 First test issue about 6 days ago
If we specify a list of comma separated fields we get those fields in JSON format:
$ gh issue list --json number,title,body
[
{
"body": "second",
"number": 2,
"title": "second issue"
},
{
"body": "💯 bien!",
"number": 1,
"title": "First test issue"
}
]
Introduction to gh api
Authentication Token
Go to github.com/settings/tokens
to generate a new token for gh and set then environment variable
GITHUB_TOKEN (export GITHUB_TOKEN= ...)
Para generar el token:
user -> settings -> developer settings -> Personal access tokens
o mas rápido vete a https://github.com/settings/tokens
Una vez se tiene un token:
# authenticate against github.com by reading the token from a file
$ gh auth login --with-token < mytoken.txt
También es posible autenticarse con el browser usando la opción -w:
➜ graphql-examples git:(main) ✗ gh auth login -w
! First copy your one-time code: F4D5-59E6
- Press Enter to open github.com in your browser...
Esto abre el browser, nos pide la contraseña que aparece arriba
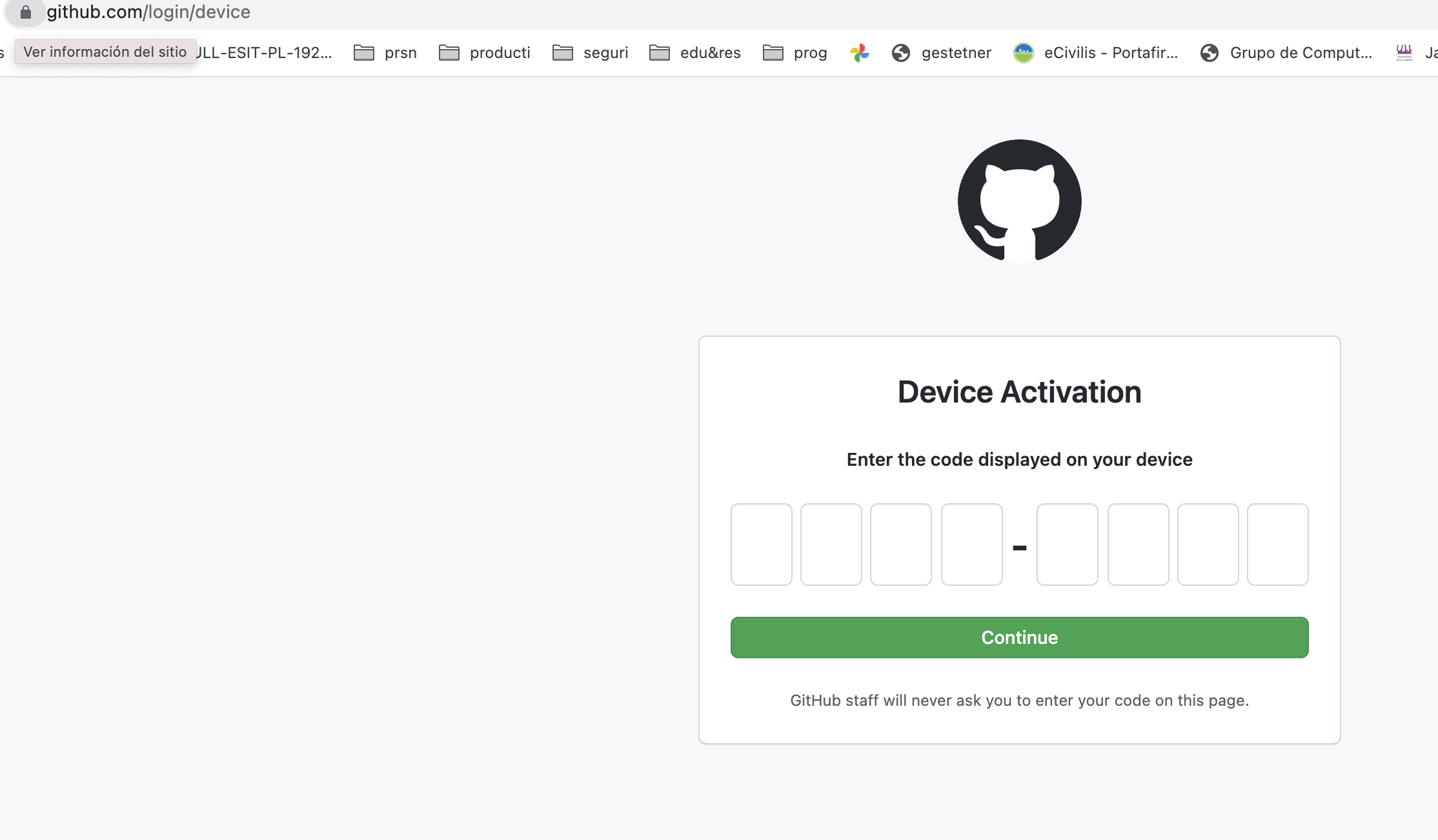
y nos pide confirmar los permisos.
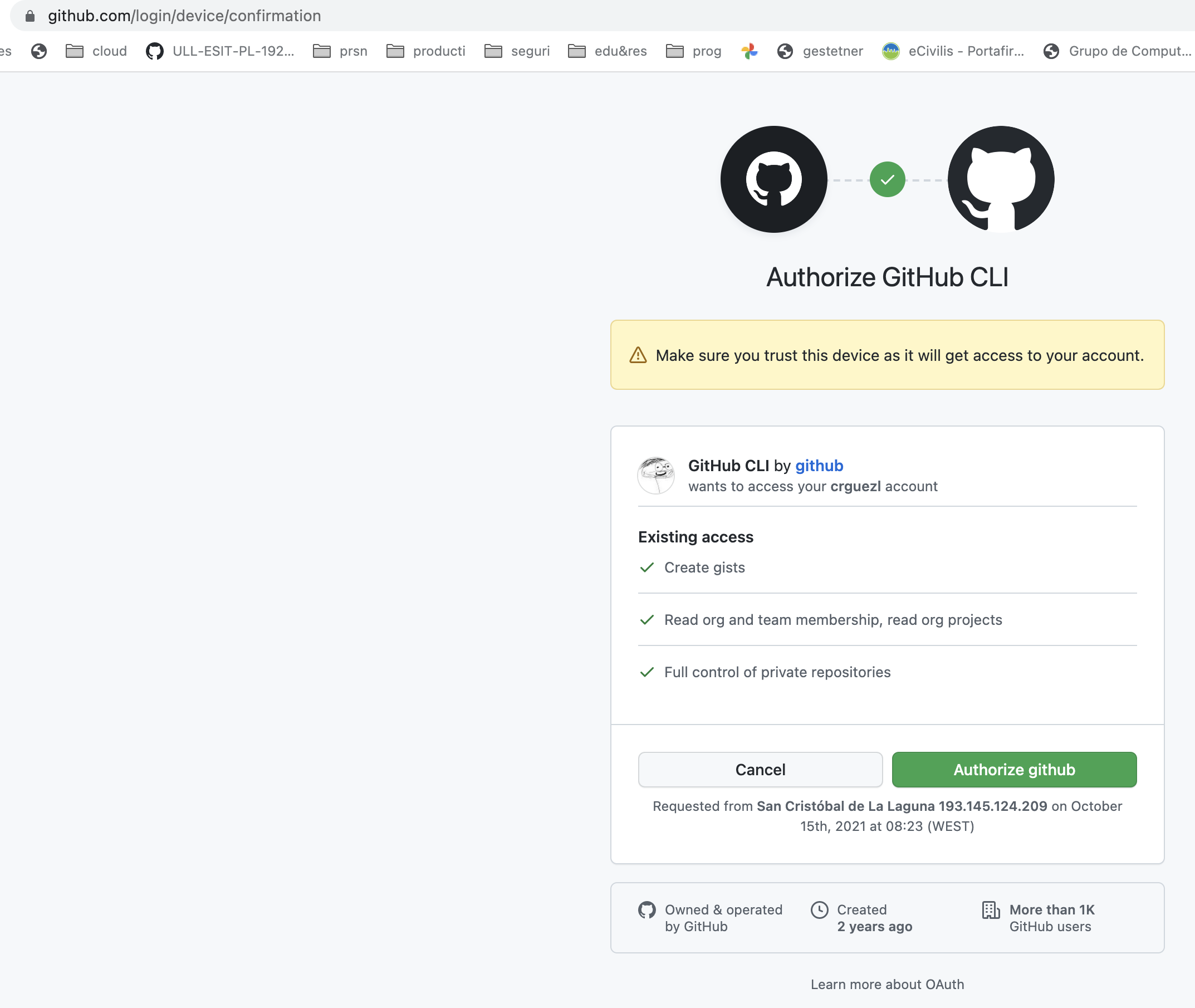
Example: Issues of a repo
Placeholder values :owner, :repo, and :branch in the endpoint argument will get replaced with values from the repository of the current directory.
$ gh api repos/:owner/:repo/issues
[
{
"url": "https://api.github.com/repos/ULL-MII-SYTWS-1920/ull-mii-sytws-1920.github.io/issues/5",
"repository_url": "https://api.github.com/repos/ULL-MII-SYTWS-1920/ull-mii-sytws-1920.github.io",
"labels_url": "https://api.github.com/repos/ULL-MII-SYTWS-1920/ull-mii-sytws-1920.github.io/issues/5/labels{/name}",
"comments_url": "https://api.github.com/repos/ULL-MII-SYTWS-1920/ull-mii-sytws-1920.github.io/issues/5/comments",
"events_url": "https://api.github.com/repos/ULL-MII-SYTWS-1920/ull-mii-sytws-1920.github.io/issues/5/events",
"html_url": "https://github.com/ULL-MII-SYTWS-1920/ull-mii-sytws-1920.github.io/issues/5",
"id": 715027457,
"node_id": "MDU6SXNzdWU3MTUwMjc0NTc=",
"number": 5,
"title": "tema0-presentacion/practicas/pb-gh-campus-expert/",
"user": {
...
}
...
}
]
We can pipe the output to jq or use the -q or --jq option of gh api:
$ gh api repos/:owner/:repo/issues | jq '.[0] | .title'
"tema0-presentacion/practicas/pb-gh-campus-expert/"
Of course, we can explicit the repo and owner. For example:
➜ gh api repos/ULL-MII-SYTWS-2021/p01-t1-iaas-alu0101040882/issues | jq '.[0] | .user.login, .body'
"crguezl"
"Hola @alu0101040882, \r\n\r\nVeo que alguno ya está trabajando en la práctica de
POST Example
Let us see an example using the POST method. We will start from this curl example
in the GitHub API getting started guide:
$ curl -i -H "Authorization: token 5199831f4dd3b79e7c5b7e0ebe75d67aa66e79d4" \
-d '{ \
"name": "blog", \
"auto_init": true, \
"private": true, \
"gitignore_template": "nanoc" \
}' \
https://api.github.com/user/repos
and let us adapt to gh api. We use -X or --method stringto set the HTTP method for the request (default GET) and -fto set the fields:
➜ /tmp gh api -X POST -f name=repo-prueba-gh-api -f private=true /user/repos
This way we have created a private repo inside the user scope:
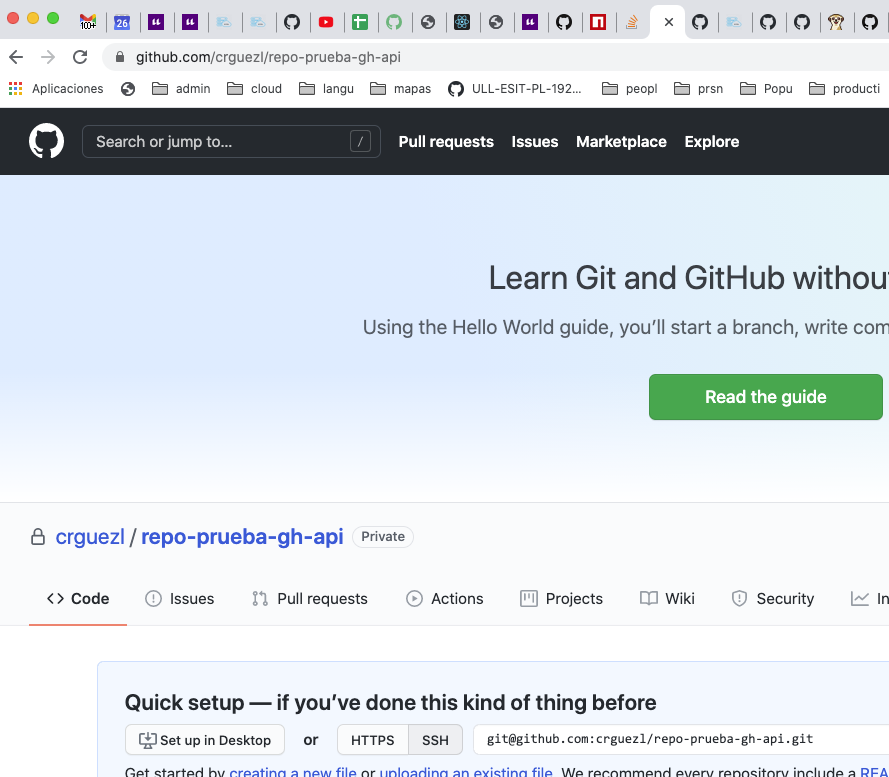
➜ input-option git:(master) ✗ gh repo-delete crguezl/repo-prueba-gh-api
➜ input-option git:(master) ✗ gh api -f name=repo-prueba-gh-api -f private=true /user/repos
Pagination
The option --paginateallow us to make additional HTTP requests to fetch
all pages of results. Here is an example.
➜ gh alias set get-repos 'api /orgs/$1/repos'
- Adding alias for get-repos: api /orgs/$1/repos
✓ Added alias.
➜ gh alias list
co: pr checkout
get-repos: api /orgs/$1/repos
➜ gh get-repos ULL-MII-SYTWS-2021
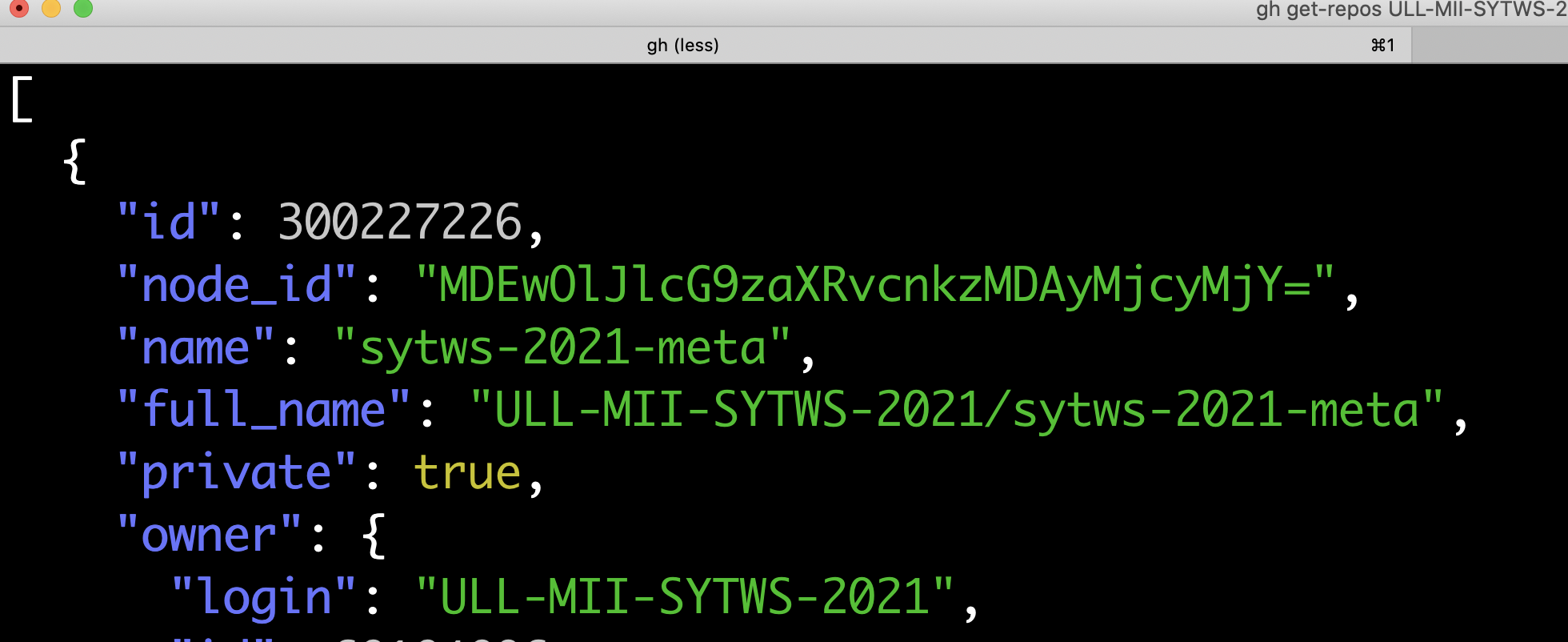
Now we can pipe the output to jq to get the names of the repos:
➜ gh get-repos ULL-MII-SYTWS-2021 | jq '.[].full_name' -
"ULL-MII-SYTWS-2021/sytws-2021-meta"
"ULL-MII-SYTWS-2021/sytws2021-private"
"ULL-MII-SYTWS-2021/books-shared"
"ULL-MII-SYTWS-2021/p01-t1-iaas-fcohdezc"
"ULL-MII-SYTWS-2021/p01-t1-iaas-crguezl"
"ULL-MII-SYTWS-2021/p01-t1-iaas-alu0100886870"
...
Let ask for the repos in the PL organization for the course 19/20:
➜ gh api /orgs/ULL-ESIT-PL-1920/repos | jq '.[] | .name' | wc
30 30 1088
It gave us 30 repos. There are much more than that in that organization.
If we use --paginate the request takes a long time and gives us near a thousand repos:
➜ gh api --paginate /orgs/ULL-ESIT-PL-1920/repos | jq '.[] | .name' | wc
990 990 32868
Templates for the output
The option -t, --template stringof gh api
allows to format the response using a Go template.
Here is an example of template:
➜ gh-learning git:(master) ✗ cat template.gotemplate
Title: {{range .}}{{.title}}
Labels: ({{.labels | pluck "name" | join ", " | color "yellow"}})
Body: {{.body}}
{{end}}
and let us use it:
➜ gh-learning git:(master) ✗ gh api repos/crguezl/learning-bash/issues --template "$(cat template.gotemplate)"
Title: issue de prueba
Labels: (bug, documentation, duplicate, enhancement, help wanted, good first issue, invalid, question)
Body: 👍 blah ...
The Labels appear in yellow.
- Véase gh formatting
Introduction to gh alias
➜ gh alias set <alias> <expansion> [flags]
Declare a word as a command alias that will expand to the specified command(s).
The expansion may specify additional arguments and flags. If the expansion
includes positional placeholders such as $1, $2, etc., any extra arguments
that follow the invocation of an alias will be inserted appropriately.
If --shell is specified, the alias will be run through a shell interpreter (sh). This allows you
to compose commands with | or redirect with >. Note that extra arguments following the alias
will not be automatically passed to the expanded expression. To have a shell alias receive
arguments, you must explicitly accept them using $1, $2, etc., or $@ to accept all of them.
Platform note: on Windows, shell aliases are executed via sh as installed by Git For Windows. If
you have installed git on Windows in some other way, shell aliases may not work for you.
Quotes must always be used when defining a command as in the examples.
Simple Examples
$ gh alias set pv 'pr view'
$ gh pv -w 123
#=> gh pr view -w 123
$ gh alias set bugs 'issue list --label="bugs"'
$ gh alias set epicsBy 'issue list --author="$1" --label="epic"'
$ gh epicsBy vilmibm
#=> gh issue list --author="vilmibm" --label="epic"
$ gh alias set --shell igrep 'gh issue list --label="$1" | grep $2'
$ gh igrep epic foo
#=> gh issue list --label="epic" | grep "foo"
Example search for members of an organization
Este request nos da un JSON con informacion sobre los miembros de una org:
gh alias set org-members api --paginate "/orgs/$1/members"
Por ejemplo:
✗ gh org-members ULL-MII-SYTWS-2122 | jq '.[] | .url, .id, .login'
"https://api.github.com/users/alu0100898293"
22496375
"alu0100898293"
"https://api.github.com/users/alu0101102726"
37936358
"alu0101102726"
"https://api.github.com/users/crguezl"
1142554
"crguezl"
"https://api.github.com/users/PaulaExposito"
56047765
"PaulaExposito"
"https://api.github.com/users/Pmolmar"
45513418
"Pmolmar"
A partir de este alias podemos construir sub-alias:
✗ gh alias set my-orgs-names --shell "gh my-orgs --jq '.[].organization.login'"
Example: Search for repos inside an organization
Let us search for repos inside our organization using GitHub API v3:
➜ gh api '/search/repositories?q=iaas+org:ULL-MII-SYTWS-2021+in:name'
Here is the JSON with the full output.
- See the SEARCH section of the REST API GitHub docs to know more about the API.
- See section Search Repositories for more info on how to search for repos
Now we can use gh alias set to make an alias get-lab to get the repos:
➜ gh alias set get-labs 'api /search/repositories?q=$2+org:$1+in:name'
- Adding alias for get-labs: api /search/repositories?q=$2+org:$1+in:name
✓ Added alias.
➜ gh alias list
co: pr checkout
get-labs: api /search/repositories?q=$2+org:$1+in:name
And now we can use it:
➜ gh get-labs ULL-MII-SYTWS-2021 iaas
Next we can pipe the output to jq to get the names of the repos and the date of the last push:
➜ gh get-labs ULL-MII-SYTWS-2021 iaas | jq '.items[] | .name, .pushed_at'
"p01-t1-iaas-juanchojbarroso"
"2020-10-21T15:58:32Z"
"p01-t1-iaas-alu0101040882"
"2020-10-17T16:53:39Z"
"p01-t1-iaas-fcohdezc"
"2020-10-06T17:51:52Z"
"p01-t1-iaas-crguezl"
"2020-10-19T13:50:13Z"
"p01-t1-iaas-alu0100886870"
"2020-10-21T17:05:08Z"
"p01-t1-iaas-lardabi"
"2020-10-06T18:01:16Z"
We can improve it by writing a script:
➜ cat ~/bin/repos
#!/bin/bash
ORG=ULL-MII-SYTWS-2021
ASSIGNMENT=iaas
if [[ $# -gt 0 ]] ; then
ASSIGNMENT=$1
fi
if [[ $# -gt 1 ]] ; then
ORG=$2
fi
# echo $ASSIGNMENT $ORG
gh api --paginate /search/repositories?q=$ASSIGNMENT+org:$ORG+in:name |
jq '.items[] | .name, .pushed_at' |
sed 'N;s/\n/ => /'
Let us make an alias for gh:
➜ gh alias set --shell get-repos 'repos $1 $2'
- Adding alias for get-repos: repos $1 $2
✓ Changed alias get-repos from !repos to !repos $1 $2
Watch the use of single quotes.
Let us use our new alias:
➜ apuntes git:(curso2021) gh get-repos TFA ULL-ESIT-PL-1920
"tfa-module-miguel-tfa" => "2020-09-04T09:40:57Z"
"tfa-daniel-tfa" => "2020-06-02T14:00:30Z"
"tfa-manuel-jorge-tfa" => "2020-09-13T21:40:24Z"
"tfa-basilio-tfa" => "2020-07-14T06:49:29Z"
"tfa-alien-tfa" => "2020-09-05T07:35:52Z"
"tfa-miguel-angel-tfa" => "2020-09-15T13:19:47Z"
"tfa-esther-sergio-tfa" => "2020-07-10T08:53:04Z"
...
GraphQL Examples
GraphQL is a query language for web services APIs and a runtime for fulfilling those queries with your existing data. GraphQL provides a complete and understandable description of the data in your API, gives clients the power to ask for exactly what they need and nothing more.
Example: Number of repos in an Organization
gh api graphql --paginate --field query=@org-num-repos.gql --jq .data.organization.repositories.totalCount
These are the contents of the file org-num-repos.gql:
query {
organization(login: "ULL-MII-SYTWS-2122") {
repositories {
totalCount
}
}
}
Execution:
✗ source org-num-repos.bash
17
Getting my repos
➜ graphql-learning git:(main) ✗ gh config set pager cat
➜ graphql-learning git:(main) ✗ cat my-repos.bash
gh api graphql --paginate -F number_of_repos=3 --field query=@my-repos.gql
In this example $number_of_repos is a variable that is set to 3 inside the command using the option -F number_of_repos=3
➜ graphql-learning git:(main) ✗ cat my-repos.gql
query($number_of_repos:Int!){
viewer {
name
repositories(last: $number_of_repos) {
nodes {
name
}
}
}
}
Here is the output of an execution:
➜ graphql-learning git:(main) ✗ gh api graphql --paginate -F number_of_repos=3 --field query=@my-repos.gql
{
"data": {
"viewer": {
"name": "Casiano Rodriguez-Leon",
"repositories": {
"nodes": [
{
"name": "asyncmap-crguezl"
},
{
"name": "gh-clone-org"
},
{
"name": "learning-graphql-with-gh"
}
]
}
}
}
}
Example: Getting issues
Follows an example of query using GraphQL (see The Example query in GitHub Docs).
We can set the GraphQL query in a separated file:
➜ bin git:(master) cat gh-api-example.graphql
query {
repository(owner:"ULL-MII-SYTWS-2021", name:"p01-t1-iaas-alu0101040882") {
issues(last:2, states:OPEN) {
edges {
node {
title
url
labels(first:5) {
edges {
node {
name
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
To learn more, see the tutorial Forming calls with GraphQL .
Looking at the composition line by line:
query {
Because we want to read data from the server, not modify it, query is the root operation. (If you don’t specify an operation, query is also the default.)
repository(owner:"ULL-MII-SYTWS-2021", name:"p01-t1-iaas-alu0101040882")
To begin the query, we want to find a repository object.
The schema validation indicates this object requires
- an
owner - and a
nameargument.
A schema defines a GraphQL API’s type system. It describes the complete set of possible data (objects, fields, relationships, everything) that a client can access
issues(last:2, states:OPEN) {
A field is a unit of data you can retrieve from an object. As the official GraphQL docs say: The GraphQL query language is basically about selecting fields on objects.
To account for all issues in the repository, we call the issues object.
Some details about the issues object:
The docs tell us this object has the type IssueConnection.
Schema validation indicates this object requires a last or first number of results as an argument, so we provide 2.
The docs also tell us this object accepts a states argument, which is an IssueState enum that accepts OPEN or CLOSED values.
To find only open issues, we give the states key a value of OPEN.
edges {
Edges represent connections between nodes. When you query a connection, you traverse its edges to get to its nodes.
We know issues is a *connection** because the Doc says it has the IssueConnection type.
Connections let us query related objects as part of the same call. With connections, we can use a single GraphQL call where we would have to use multiple calls to a REST API.
To retrieve data about individual issues, we have to access the node via edges.
node {
Here we retrieve the node at the end of the edge.
The IssueConnection docs indicate the node at the end of the IssueConnection type is an Issue object.
Now that we know we’re retrieving an Issue object, we can look at the docs for issue and specify the fields we want to return:
title
url
labels(first:5) {
edges {
node {
name
}
}
}
Here we specify the title, url, and labels fields of the Issue object.
The labels field has the type LabelConnection. As with the issues object, because labels is a connection, we must travel its edges to a connected node: the label object. At the node, we can specify the label object fields we want to return, in this case, name.
In gh, the --field flag behaves like --raw-field with magic type conversion based on the format of the value:
- literal values “true”, “false”, “null”, and integer numbers get converted to appropriate JSON types;
- placeholder values “:owner”, “:repo”, and “:branch” get populated with values from the repository of the current directory;
- if the value starts with “@”, the rest of the value is interpreted as a filename to read the value from. Pass “-“ to read from standard input.
For GraphQL requests, all fields other than “query” and “operationName” are interpreted as GraphQL variables.
Execution:
➜ gh api graphql --paginate -F query=@gh-api-example.graphql | jq .
{
"data": {
"repository": {
"issues": {
"edges": [
{
"node": {
"title": "Revisión",
"url": "https://github.com/ULL-MII-SYTWS-2021/p01-t1-iaas-alu0101040882/issues/2",
"labels": {
"edges": [
{
"node": {
"name": "enhancement"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
Mutation Example
➜ graphql-learning git:(main) cat findissueid.bash
gh api graphql --paginate --field query=@findissueid.gql
➜ graphql-learning git:(main) cat findissueid.gql
query FindIssueID {
repository(owner:"crguezl", name:"learning-graphql-with-gh") {
issue(number:2) {
id
}
}
}
➜ graphql-learning git:(main) cat viewissue.bash
gh issue -R crguezl/learning-graphql-with-gh view $@%
➜ graphql-learning git:(main) cat addreactiontoissue.bash
#!/bin/bash
# See
# https://docs.github.com/en/graphql/guides/forming-calls-with-graphql#example-mutation
# and
# https://docs.github.com/en/enterprise-server@3.0/graphql/guides/forming-calls-with-graphql
# for a list of supported emojis
gh api graphql --paginate --field query=@addreactiontoissue.gql
➜ graphql-learning git:(main) cat addreactiontoissue.gql
mutation AddReactionToIssue {
addReaction(input:{subjectId:"I_kwDOGLyMF84838wt",content:ROCKET}) {
reaction {
content
}
subject {
id
}
}
}
Extensions
GitHub CLI extensions are repositories that provide additional gh commands.
The name of the extension repository must start with “gh-“ and it must contain an executable of the same name. All arguments passed to the gh
- gh extension subcommands
- create: Create a new extension
- install: Install a gh extension from a repository
- list: List installed extension commands
- remove: Remove an installed extension
- upgrade: Upgrade installed extensions
inside my mac the gh extensions repos are stored in ~/.local/share/gh/extensions/
➜ gh-learning git:(master) ✗ ls -la ~/.local/share/gh/extensions/
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 7 casianorodriguezleon staff 224 6 oct 10:11 .
drwxr-xr-x 3 casianorodriguezleon staff 96 17 sep 13:07 ..
drwxr-xr-x 7 casianorodriguezleon staff 224 6 oct 10:11 gh-clone-org
drwxr-xr-x 5 casianorodriguezleon staff 160 1 oct 17:18 gh-delete-repo
lrwxr-xr-x 1 casianorodriguezleon staff 89 1 oct 16:23 gh-gitpod-open -> /Users/casianorodriguezleon/campus-virtual/shared/2021learning/gh-learning/gh-gitpod-open
drwxr-xr-x 8 casianorodriguezleon staff 256 17 sep 13:07 gh-gp
drwxr-xr-x 8 casianorodriguezleon staff 256 17 sep 13:19 gh-project
See also:
Examples of extensions
gh-clone-org
How it works:
[/tmp/chuchu]$rm gh clone-org -s set-up -y -n
Retrieving the list of repositories: search/repositories?q=org%3AULL-MII-SYTWS-2122%20set-up
This would have cloned the following 5 repositories to /tmp/chuchu:
ULL-MII-SYTWS-2122/set-up-alu0100898293
ULL-MII-SYTWS-2122/set-up-PaulaExposito
ULL-MII-SYTWS-2122/set-up-alu0101102726
ULL-MII-SYTWS-2122/set-up-crguezl
ULL-MII-SYTWS-2122/set-up-Pmolmar
gh-submodule-add
This is a extension written in Node.js
Running Manually GitHub Workflows with gh
Cambiando los permisos de GITHUB_TOKEN
En el contenedor de CodeSpaces tenemos gh instalada.
Tanto ghcomo CodeSpaces usan
la variable de entorno GITHUB_TOKEN para hacer uso de la API.
De hecho GITHUB_TOKEN es una de las muchas variables de entorno que gh usa. Otras variables interesantes son GH_REPO y GH_CONFIG_DIR.
Pero, por defecto, el token en GITHUB_TOKEN no tiene permisos suficientes
para acceder a otros repos distintos del de trabajo.
Se plantea así el problema de cambiarle los permisos al token.
En las ocasiones en las que queremos cambiar los scopes de GITHUB_TOKEN podemos proceder así:
En primer lugar, tienes que desactivar GITHUB_TOKEN, de lo contrario gh cli lo usará y omitirá la autenticación
unset GITHUB_TOKEN
Después usaremos gh auth login para cambiar los scopes del per-host token oauth_token de gh.
Las opciones que son interesantes de gh auth login son:
-h,--hostname stringThe hostname of the GitHub instance to authenticate with-s,--scopes stringsAdditional authentication scopes to request-w, --webOpen a browser to authenticate
Siempre podemos obtener el per-host oauth token así:
✗ gh config get -h github.com oauth_token
gho_w-blah-blah-blah
o bien accediendo directamente al fichero de configuración per-host de gh:
✗ ls -a ~/.config/gh/
. .. config.yml hosts.yml
✗ grep -i oauth ~/.config/gh/hosts.yml
oauth_token: gho_w-blah-blah-blah
Si queremos modificar los permisos del oauth_token deberemos hacer algo así:
gh auth login --hostname 'github.com' --scopes 'repo,admin:org,delete_repo,codespace,read:packages'
Podemos obtener el valor de este token y almacenarlo en una variable con:
token="$(gh config get -h github.com oauth_token)"
export GITHUB_TOKEN="$token"
List of scopes: https://docs.github.com/en/developers/apps/building-oauth-apps/scopes-for-oauth-apps#available-scopes
References
- Repo crguezl/learning-graphql-with-gh
- gh manual
- GitHub REST API
- Getting started with the REST API
- Scripting with GitHub CLI by Mislav Marohnić
- Blog: GitHub CLI is Now Available: Here’s Why You Should Be Excited by Kasun Rajapakse
- An Introduction to GraphQL via the GitHub API by Derek Haynes *GitHub GraphQL Playground
Tus Comentarios

All the work in this pages (including PDFs authored by us) is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.